Surgical treatment is proposed in case of failure of conservative treatment. It consists of restoring the normal sliding of the FHL tendon by opening the osteofibrous tunnel situated at the back of the ankle. The intervention is called: endoscopic tenolysis of the FHL by section of the retrotalar pulley. This gesture is sometimes associated with the resection of an accessory bone (os trigonum) or a bone outgrowth (bulky posterior lateral tubercle) that participates in the conflict. This operation can be performed arthroscopically while you are lying on your stomach (in the prone position).
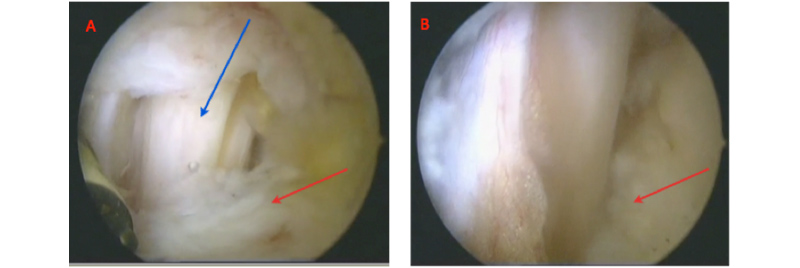
Arthroscopy is a surgical technique that allows visualization of the tendon, pulley, ankle and subtalar joints by making small incisions. The arthroscope is a tube of a few millimeters in diameter, equipped with an optical and a lighting system; it is coupled with a mini video camera connected to a television screen in High Definition. The arthroscope is introduced through a posterolateral approach located on the outer side of the Achilles tendon. In this way, we can observe the subtalar articulation and individualize the retro-talial pulley of the hallux’s long flexor.

By means of an approach located on the internal slope of the Achilles tendon, instruments are introduced which are used to incise the pulley in contact with the slope until a free tendinous sliding is achieved. This gesture also frees the subtalar joint locked by the tenodesis effect. After a final check of the haemostasis, the arthroscopic incisions are sutured.
The results after the surgical treatment are permanent. Indeed, once the tendon is released, recurrence is highly unlikely to reappear (less than 0.5%). As a result, rebalancing during walking is restored in a sustainable way. This is the reason why it is necessary to walk with new shoes after surgery.
If I have to be operated
Participation of your family doctor
Once the decision to operate has been established, your doctor can be informed and if necessary will organize the necessary examinations to complete the preoperative evaluation of the anesthesiologist. This intervention does not require, in principle, any particular examination.
You will receive a letter of invitation from the Clinique Bois Cerf with information regarding:
Pre-anesthesia consultation
Before surgery, you will be seen by one of our anesthetist doctors who will discuss your medical history with you before proceeding to a clinical examination. You can then discuss the different anesthesia methods available and choose the most suitable for your specific case (general anesthesia, epidural anesthesia, spinal anesthesia, nerve blocks, combined anesthesia).
When to arrive at the Clinique Bois Cerf reception?
On the day of the intervention.
You can usually return home the next day after a physiotherapy session during which our physiotherapists will teach you the exercises to do and the precautions to take.
Surgery
What to bring with you:
- Your personal belongings
- • Books/magazines if you like to read
- Music player (which you can bring to the operating room)
- • Optimism and energy, (we’ll take care of the rest!)
Pain control after the operation
This procedure is generally tolerated well in terms of pain. It is possible to move about the same day and the wound dressing is changed the next morning. Your anesthesiologist doctor will supervise the post-operative pain treatment.
Recovery
The day after the procedure, you will be able to walk without difficulty. Walking is done taking small steps at first, then quite normally after a few days.
Physio management is complemented by proprioception exercises on one foot, toning exercises for the foot muscles and overall knee and pelvic stabilization exercises. It is a combined treatment that comprises joint mobilization, stretching, muscle-toning and foot stabilization in contact with the ground. Osteopathy, physiotherapy and podiatry are complementary to the FHL treatment. A precise protocol that ensures free tendon glide and rebalances the entire lower limb has been studied and implemented by us. The patient is asked to refrain from strenuous activities for 4-5 days and to wait ten days before resuming any sports activities.

Potential risks
Infection
Infection is always an existing complication in orthopedic surgery but fortunately very rare (less than 0.5%) in this case. Special measures are taken to minimize these risks: systematic preoperative antibiotic therapy, operating theatres equipped with a high-speed laminar flow, a trained surgical team of orthopedics, an optimal skin preparation and a careful assessment of your condition.
In case of fever or local redness that may appear after your intervention, you must call your surgeon without delay.
Bleeding
The risk of bleeding exists but is relatively low in this procedure since an arthroscopic approach is used.
Lesion of a sensory nerve
A nerve branch located at the site of the procedure can be stretched and cause loss of sensitivity on the inner side of the heel. In most cases this complication is reversible after a few weeks.
Instability of the subtalar joint
The subtalar joint is composed of an anterior part and posterior part separated by the sinus of the tarsus. If the ligaments in this space are intact, the risk of instability is low. On the other hand, if a ligament is torn and there is a constitutional hyperlaxity, endoscopic tenolysis of FHL may in some cases lead to additional laxity of the subtalar joint.
Learn more
Endoscopic tenolysis of the flexor digitorum longus of the big toe for Functional Hallux Limitus
 EN
EN  DE
DE  ES
ES  FR
FR 